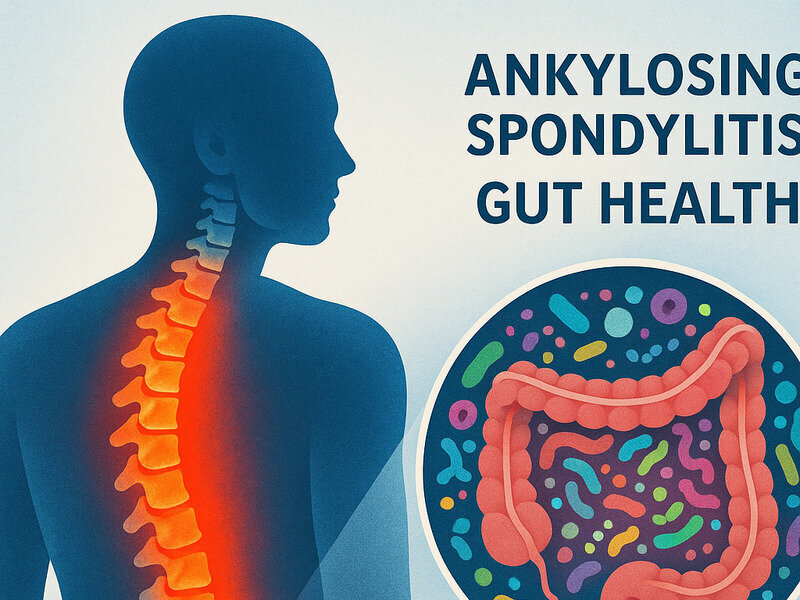
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory disease primarily affecting the spine and sacroiliac joints. It is known for causing pain and stiffness, which can lead to reduced mobility and quality of life. Recent research has highlighted a potential connection between AS and gut health, suggesting that the gut microbiome may play a significant role in the pathogenesis of this condition. This article explores the scientific evidence linking ankylosing spondylitis and gut health, examining how this relationship might influence treatment strategies.
Understanding Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis is part of a group of inflammatory diseases known as spondyloarthropathies. It primarily affects young adults, with symptoms typically appearing between the ages of 20 and 40. The prevalence of AS varies globally, with estimates suggesting it affects 0.1% to 1.4% of the population, according to the American College of Rheumatology.
The hallmark feature of AS is inflammation of the spinal joints, which can lead to fusion over time. This fusion results in a loss of flexibility and can cause a forward-stooped posture. Other sy...
Premium preview
Premium members unlock the full article—complete step-by-step routines, deeper coaching notes, and exclusive frameworks.


