Inflammation is a natural and essential part of the body's immune response. It is the process by which the immune system recognizes and removes harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and begins the healing process. However, when inflammation becomes chronic, it can lead to a host of health problems, including autoimmune diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and even cancer. While many factors contribute to inflammation, recent research has highlighted the significant role of the gut in regulating this complex process.
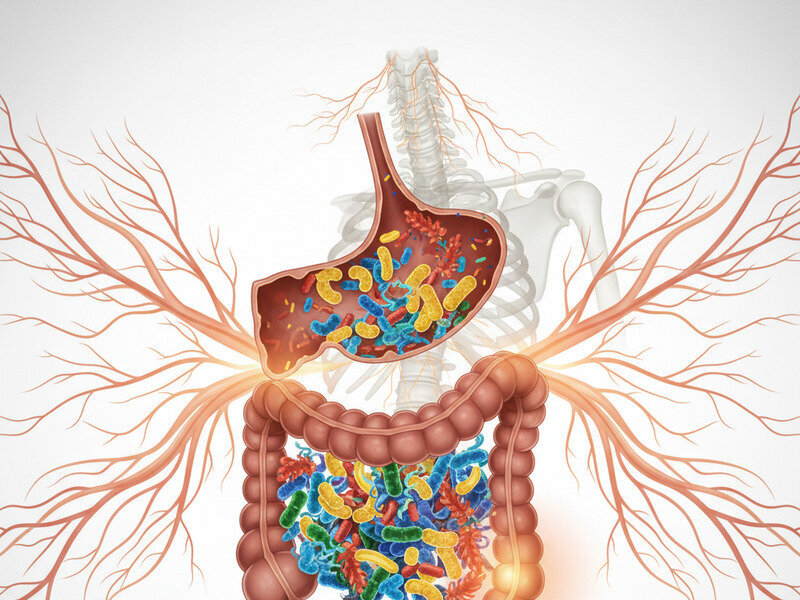
The gut, often referred to as the gastrointestinal tract, is home to trillions of microorganisms collectively known as the gut microbiota. These microorganisms include bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microbes that coexist in a delicate balance. The gut microbiota plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including digestion, metabolism, and immune system regulation. It is increasingly recognized that the gut microbiota has a profound impact on inflammation throughout the body.
The Gut Microbiota and Immune System Interaction
The interaction between the gut microbiota and the immune system is a key factor in controlling inflam...
Premium preview
Premium members unlock the full article—complete step-by-step routines, deeper coaching notes, and exclusive frameworks.


